Open-source large language models (LLMs) like LLaMA, Deepseek, Qwen and Mistral etc have surged in popularity, offering enterprises greater flexibility, cost savings, and control over their AI deployments. These models have empowered organizations to build their own AI-driven applications, from chatbots and agents to content generation and recommendation systems.
However, while these models are widely accessible, turning them into cost-efficient, production-grade APIs remains a significant challenge. Achieving low-latency, scalable inference requires more than just an optimized model—it demands a holistic system approach that spans multiple layers, from the model itself to the inference engine and the surrounding infrastructure.
Three-Layer Approach: Open Source Model, vLLM and AIBrix
Building a performant and cost-effective LLM API requires joint efforts across three key layers:
Open-Source Models: The foundation of AI applications, where model optimizations such as model architecture, Grouped Query Attention (GQA), distillation and adapter finetuning techniques improvements enhance performance and adaptability.
Inference Engines (vLLM): These provide efficient execution, KV cache management, model parallelism, attention optimization, and other optimizations that improve model serving performance.
System-Level Orchestration (AIBrix): The often-overlooked layer that determines real-world cost efficiency and scalability by handling resource scheduling, autoscaling, cache-aware routing, heterogeneity management, and multi-cluster or region resource optimization.
While model and engine-level optimizations are critical, system-level orchestration is where true cost efficiency is unlocked. Without a well-designed infrastructure, even the best inference engines struggle with real-world challenges like model distribution, autoscaling, cache-aware routing, heterogeneity etc..
Introducing AIBrix: A Cloud-Native Infrastructure for Large-Scale LLM Serving
To bridge this systme-layer gap, we introduced AIBrix—a cloud-native, open-source infrastructure toolkit designed to simplify and optimize LLM deployment. AIBrix operates at the orchestration level, serving as vLLM’s control plane to enable enterprise-grade reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. AIBrix is also a solid research platform that integrates cutting-edge research insights and features a co-designed architecture with vLLM to enhance inference efficiency. Through continuous iteration, AIBrix has evolved across two minor versions, incorporating multiple innovations.
- High-Density LoRA Management: Cost-Effective Model Adaptation
- Advanced LLM Gateway and Routing Strategies
- Unified AI Runtime with GPU Streaming Loader
- LLM-Specific Autoscaling for Performance Optimization
- External Distributed KV Cache pool
- Mix-Grain Multi-Node Inference Orchestration
- Cost efficient and SLO-driven Heterogenous Serving
- Accelerator Diagnostic and Failure Mockup Tools
AIBrix Architecture
AIBrix contains both control plane components and data plane components, 100% built on Kubernetes, following a fully cloud-native design to ensure seamless scalability, reliability, and resource efficiency. It leverages Kubernetes’ existing capabilities, such as custom resources, controller mechanisms, and dynamic service discovery etc to provide a robust infrastructure for large-scale LLM serving.
The components of the control plane manage the registration of model metadata, autoscaling, model adapter registration, and enforce various types of policies. Data plane components provide configurable components for dispatching, scheduling, and serving inference requests, enabling flexible and high-performance model execution.
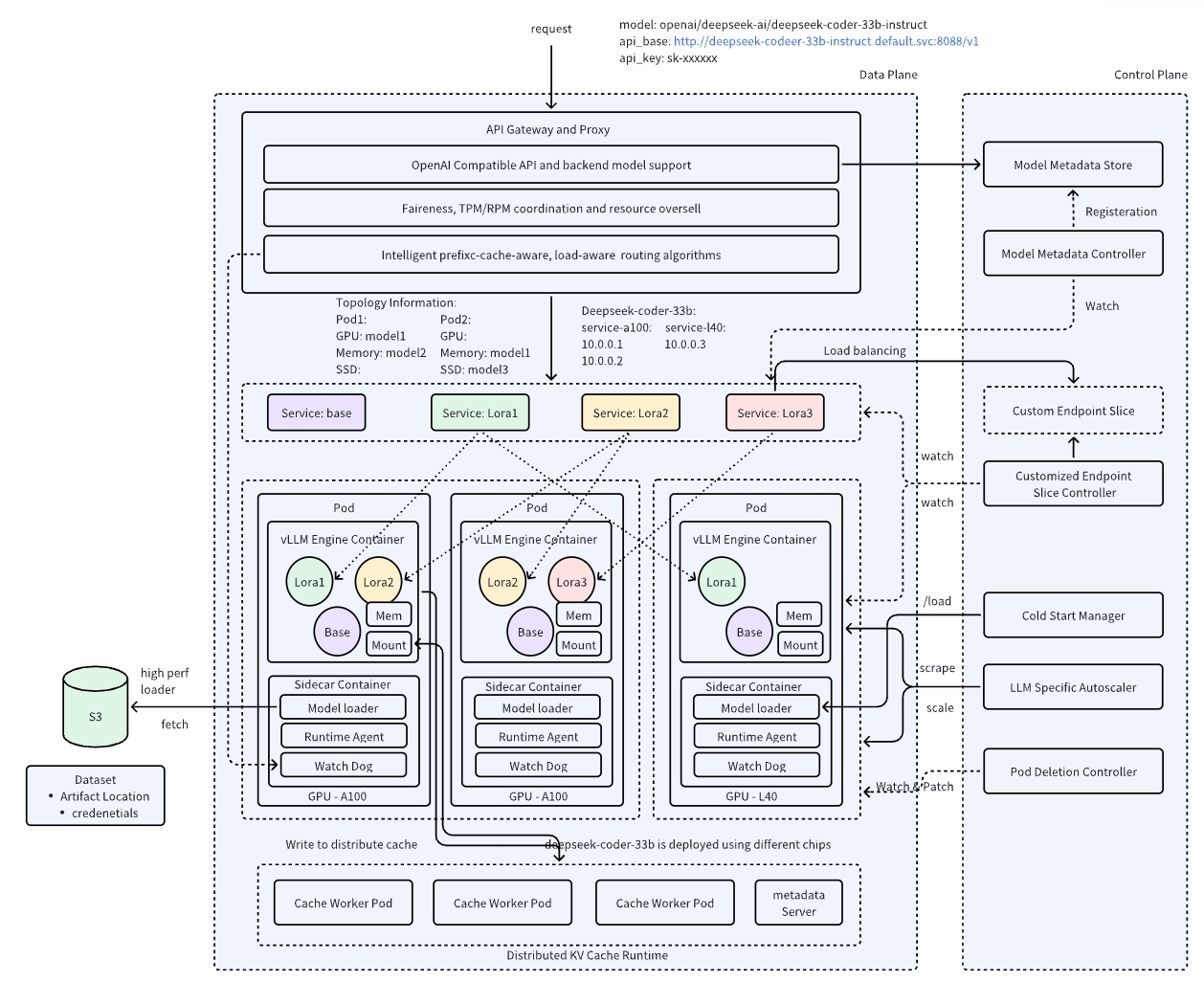
AIBrix Key Features and Innovations
AIBrix provides an infrastructure that addresses most system challenges head-on with a cohesive suite of tools and features. Here’s a look at some core components that make AIBrix a powerful solution for scalable LLM deployments
High-Density LoRA Management: Cost-Effective Model Adaptation
Deploying LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) models at scale has traditionally been constrained by static deployments, limiting flexibility and driving up costs. Most serving infrastructures treat LoRA models as fixed additions to a base model, making dynamic scaling impractical. Without resource managers’ integration, lora evictions, failure handling remain unreliable, and resource allocation becomes inefficient.
AIBrix introduces high-density LoRA management, enabling dynamic adapter loading/unloading, intelligent scheduling, and LoRA-aware routing to optimize inference efficiency. By dynamically registering LoRA adapters, we enable high-density model deployment, significantly reducing inference costs—making it an ideal solution for long-tail scenarios. AIBrix leverages Kubernetes’ built-in mechanisms, such as Service and EndpointSlice, for efficient LoRA model service discovery. We are also developing strategies to ensure models are placed on optimal pods with minimal interference. Beyond system-level improvements, we have introduced enhancements in vLLM to strengthen LoRA management capabilities. This design not only reduces operational overhead but also improves inference performance under mixed workloads.
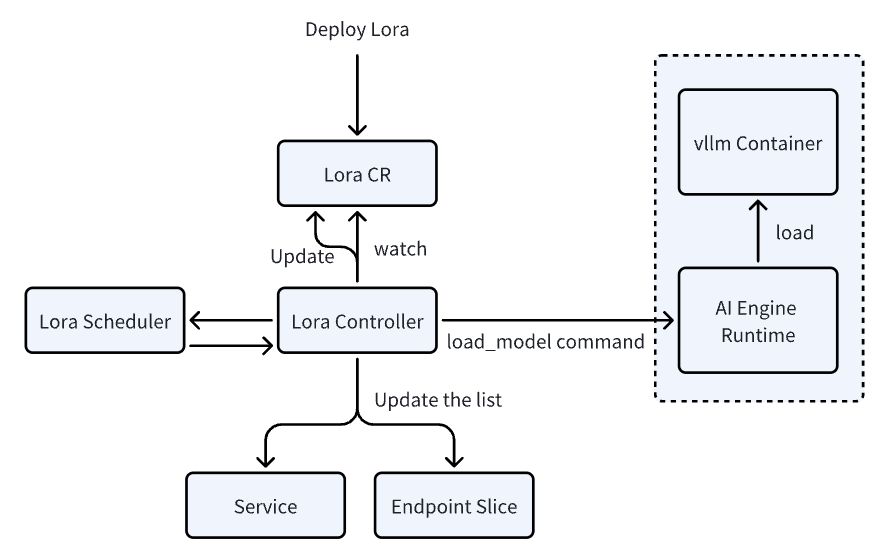
The results? A 4.7× cost reduction in low-traffic scenarios and 1.5× savings even under high demand, all while maintaining seamless performance and eliminating bottlenecks in LoRA deployment workflows.
Advanced LLM Gateway and Routing Strategies
Traditional API gateways struggle with LLM inference due to the wide variability in request complexity—from simple queries to multi-turn conversations with intricate token interactions. Generic routing fails to optimize for these nuances, causing inefficient traffic distribution and latency spikes.
AIBrix solves this with an LLM-aware gateway, extending Envoy to support instance routing, prefix-cache awareness, and least-GPU-memory-based strategies. Instead of blindly distributing requests, our routing engine analyzes token patterns, prefill cache availability, and compute overhead to optimize traffic flow. This enables advanced features and allows users to integrate custom routing strategies.
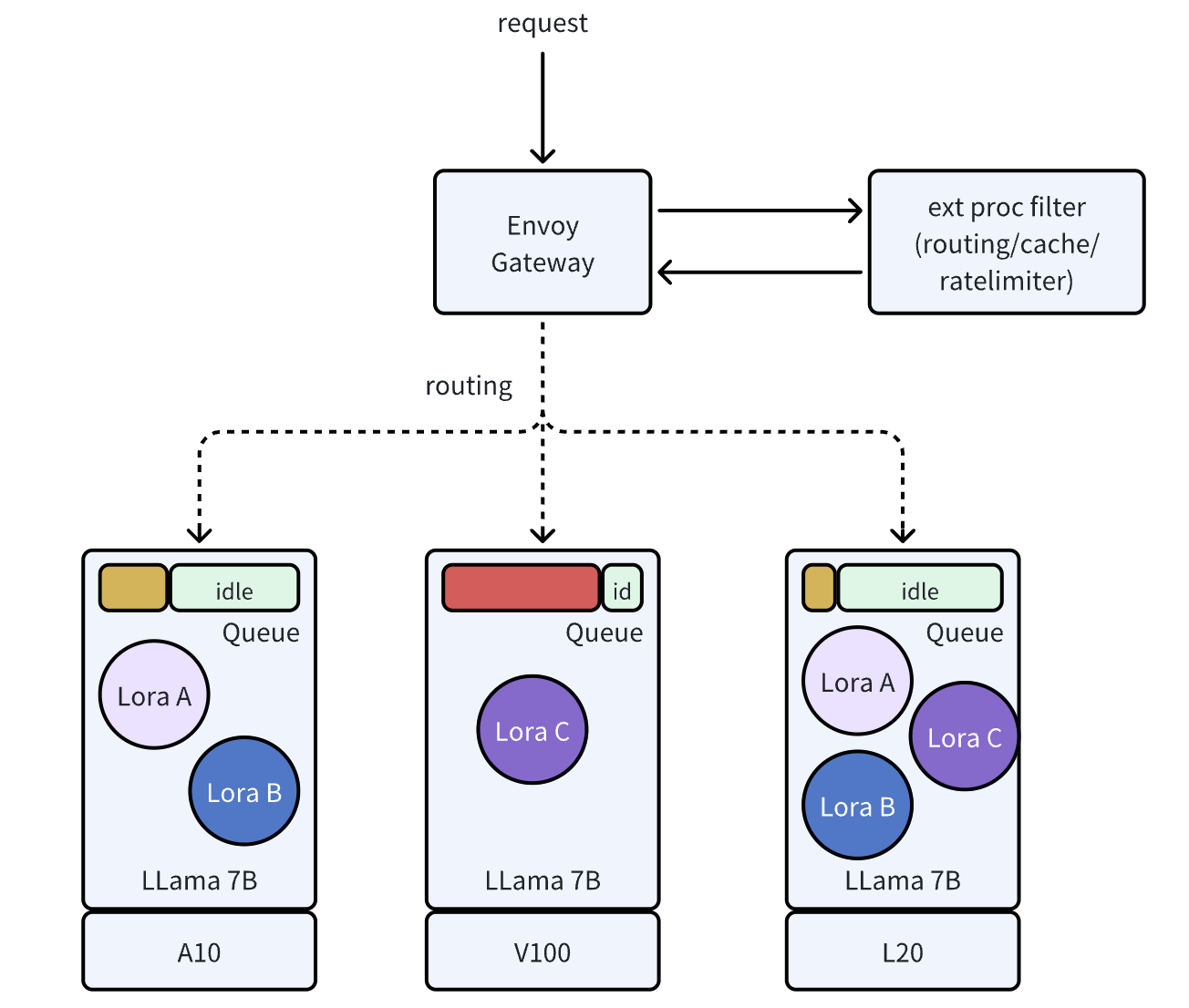
We are also collaborating with Google and Kubernetes WG-Serving on the Gateway API Inference Extension to drive scalable, standardized solutions. By selecting a fitting routing strategy, AIBrix is able to reduce mean latency by 19.2% and P99 latency by 79% on public datasets, ensuring efficient and fair LLM inference at scale.
Unified AI Runtime
AIBrix introduces a unified AI runtime and it serves as an essential bridge between the AIBrix Control Plane and inference engine pods, enabling model management, engine configuration, observability, and vendor-agnostic engine support. The runtime ensures seamless communication between the control plane and inference pods. This allows components like the LoRA adapter controller, autoscaler, and cold start manager to interact dynamically with inference containers, managing resources in a cloud-native way. The other important role is to abstract Vendor-Specific APIs and it is designed to work with diverse inference engines. Now, only vLLM is supported.
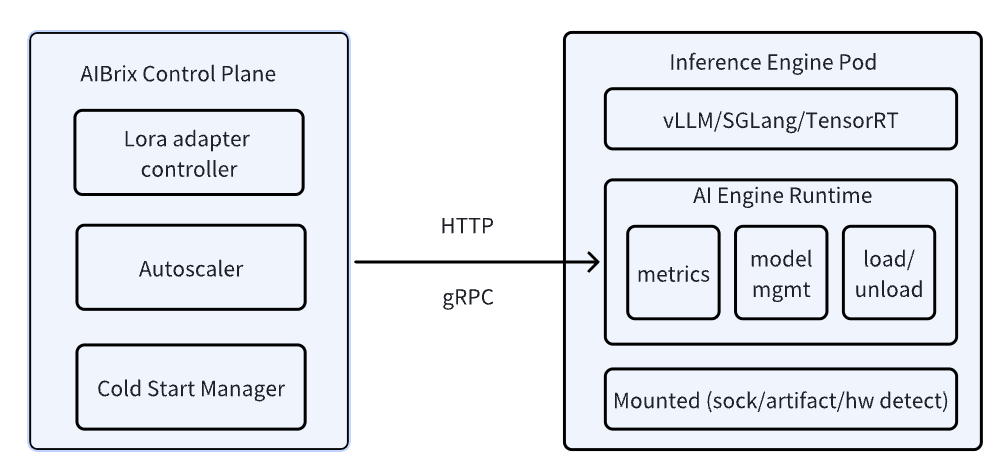
LLM-Specific Autoscaling for Performance Optimization
Autoscaling for LLM inference is challenging due to DCGM metric limitations, non-linear scaling behaviors, and the inadequacy of traditional indicators like QPS or concurrency. Request complexity and input/output size vary widely, often overwhelming systems before autoscalers can react. Additionally, large GPU images and slow model distribution introduce a 2-3 minute delay for new pods to become operational, making rapid scaling inefficient.
AIBrix tackles these issues with LLM-specific autoscaling, replacing Prometheus-based polling with sliding window metric aggregation for real-time load reporting. By leveraging advanced autoscaling algorithms like KPA , APA and our traffic distribution profiling autoscaler, our approach achieves an 11.5% reduction in latency, an 11.4% increase in token throughput, and 33% fewer scaling oscillations compared to native HPA. Looking ahead, we’re exploring token-based proactive scaling and SLO-driven autoscaling to further enhance efficiency and responsiveness.
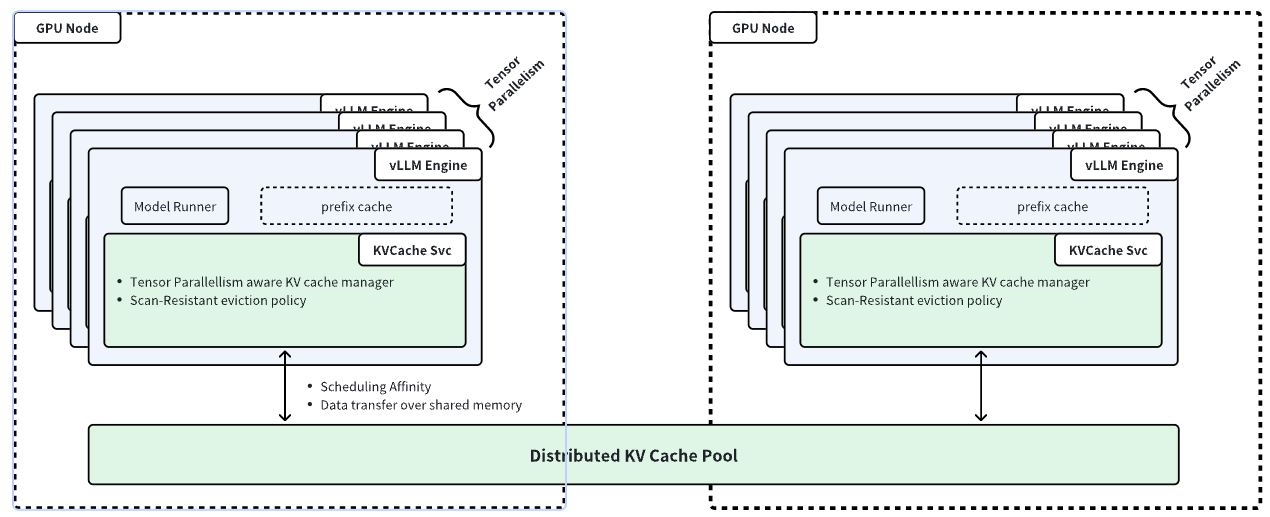
Distributed KV Cache Pool
The rising demand for large language models has intensified the need for efficient memory management and caching to optimize inference performance and reduce costs. In multi-round use cases like chatbots and agent-based systems, overlapping token sequences lead to redundant computations during the prefill phase, wasting resources and limiting throughput.
Many inference engines, such as vLLM, use built-in KV caching to mitigate this issue, leveraging idle HBM and DRAM. However, single-node KV caches face key limitations: constrained memory capacity, engine-specific storage that prevents sharing across instances, and difficulty supporting scenarios like KV migration and prefill-decode disaggregation.
AIBrix addresses these challenges with a distributed KV cache, enabling high-capacity, cross-engine KV reuse while optimizing network and memory efficiency. Our solution employs a scan-resistant eviction policy to persist hot KV tensors selectively, ensuring that network and memory usage is optimized by minimizing unnecessary data transfers, asynchronous metadata updates to reduce overhead, and cache-engine colocation for faster data transfer via shared memory.
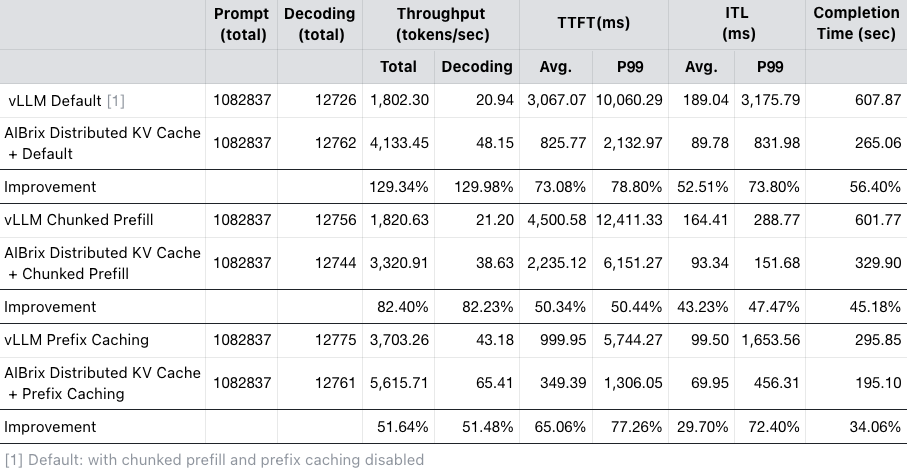
Benchmarking with Bird Text2SQL workloads shows that, even when compared to the prefix caching feature in vLLM, combining the distributed KV cache with prefix caching improves peak throughput by ~50%, reduces average and P99 TTFT by ~60% and ~70%, and lowers average and P99 ITL by ~30% and ~70%, demonstrating significant efficiency gains. A more detailed comparison is summarized in the following table.
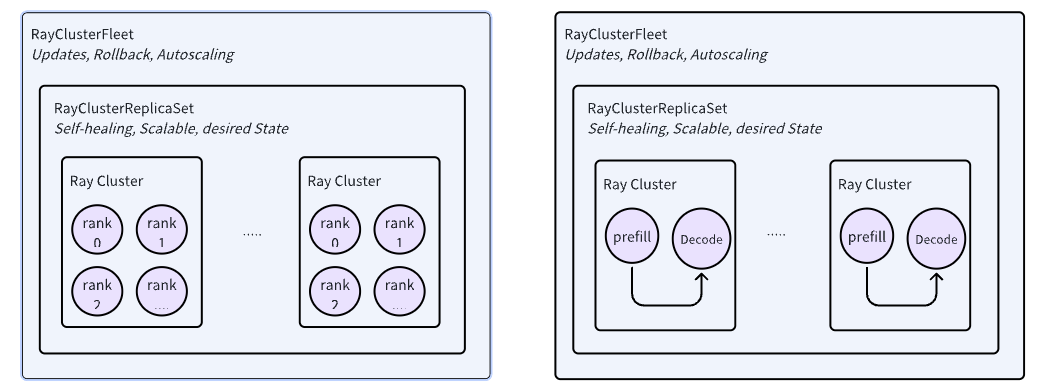
Mix-Grain Multi-Node Inference Orchestration
The release of Llama 3 (405B) and Deepseek-R1 (671B) has driven demand for multi-node inference, yet frameworks like vLLM prioritize parallelism over service-oriented needs like scaling and rolling upgrades, requiring external orchestration. In the landscape of distributed computing, both Kubernetes and Ray offer orchestration capabilities but with trade-offs: Kubernetes operators can be overly complex for fine-grained scheduling, while Ray excels in distributed communication but lacks broader resource management.
We propose a hybrid approach combining Ray for fine-grained application orchestration and Kubernetes for coarse-grained resource management, simplifying operator design while improving flexibility and efficiency. This method is informed by Bytedance’s internal experience in hosting Kubernetes and Ray workloads, addressing challenges where workload communication patterns often require frequent orchestration adjustments.
Cost-efficient and SLO-driven Heterogenous Serving
Literature such as Melange and QLM has figured out that the throughput of LLM serving under specific SLO is a function of (# input tokens, # output tokens, model) under heterogeneous GPUs environments.
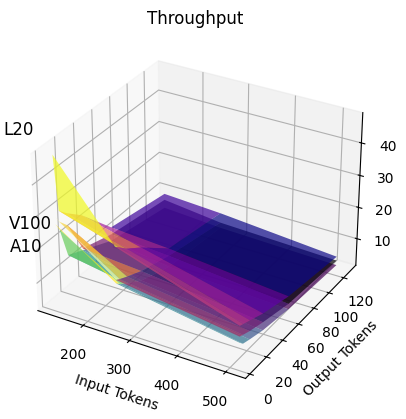 Throughputs of workload using the deepseek-coder-7b model on L20, V100 and A10 GPU
Throughputs of workload using the deepseek-coder-7b model on L20, V100 and A10 GPU
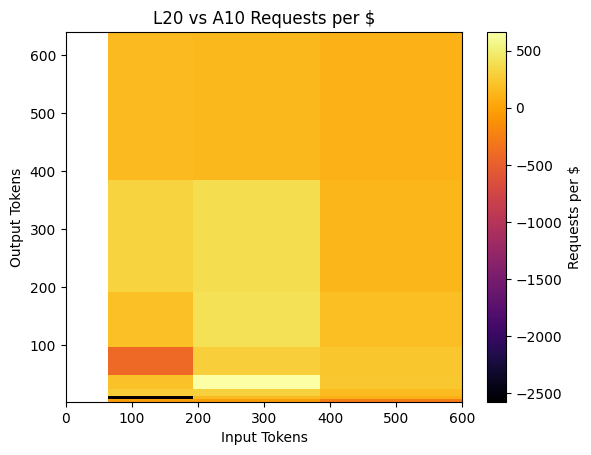 While most requests of different (# input tokens, # output tokens) pairs prefer L20 for cost-efficiency, requests of # input tokens < 200, # output tokens < 100 prefer A10.
While most requests of different (# input tokens, # output tokens) pairs prefer L20 for cost-efficiency, requests of # input tokens < 200, # output tokens < 100 prefer A10.
Furthermore, when considering requests per dollar, different GPUs exhibit varying efficiency across different input-output token distributions, even for the same model, as shown above. In addition, production users frequently face GPU availability constraints, making it difficult to consistently access the same GPU types.
To address these challenges, AIBrix introduces a GPU optimizer that works as an independent off-path component designed to optimize heterogeneous GPU serving. Below is the high-level architecture:
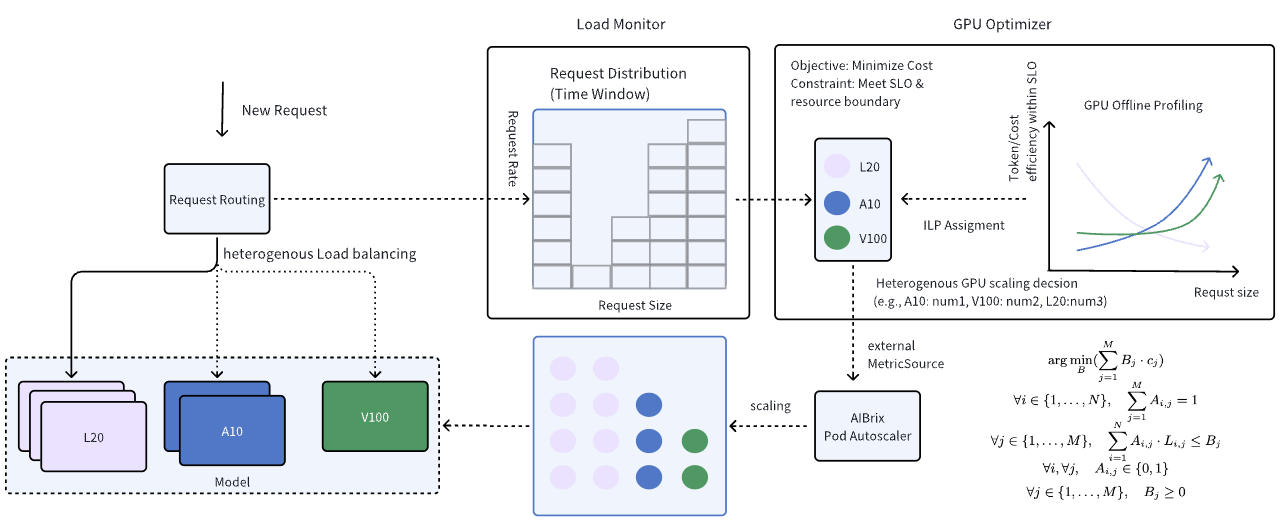
How does it work?
- The Load Monitor tracks deployment changes, assumes different deployments of the same model use different GPUs. It also analyzes statistics from the AIBrix Gateway to identify dominant workload patterns (# input/ # output tokens).
- The GPU Optimizer dynamically selects the optimal GPU combination to balance cost-efficiency while meeting SLOs.
- AIBrix’s PodAutoscaler reads external MetricSource data from the GPU Optimizer to adjust GPU allocation. Currently, the GPU optimizer supports an ILP solution proposed in Melange and needs pre-deployment profiling. AIBrix provides the necessary toolkits for workload benchmarking and profile generation.
In our experiment comparing heterogeneous workloads (using A10 and L20) against a homogeneous setup (using only L20), we evaluated a mixed dataset consisting of ShareGPT and Text2SQL workloads. Under the heterogeneous configuration, the GPU optimizer led to a latency increase of up to 20% while still remaining within the specified SLO. However, this setup reduced costs by approximately 10% compared to the homogeneous GPU deployment.
AI Accelerator Diagnostic and Failure Mockup Tools
GPU failures and performance degradation pose significant challenges in large-scale AI deployments. Silent errors, overheating, memory leaks, and intermittent failures can lead to degraded model performance, increased latency, or even system crashes. Many production users struggle with diagnosing GPU issues in heterogeneous environments, where different GPU models behave inconsistently under varying workloads.
To address these challenges, AIBrix Accelerator Tools introduces:
- GPU Diagnostics & Issue Identification – Automates fault detection, helping users identify and resolve GPU-related performance issues before they impact workloads.
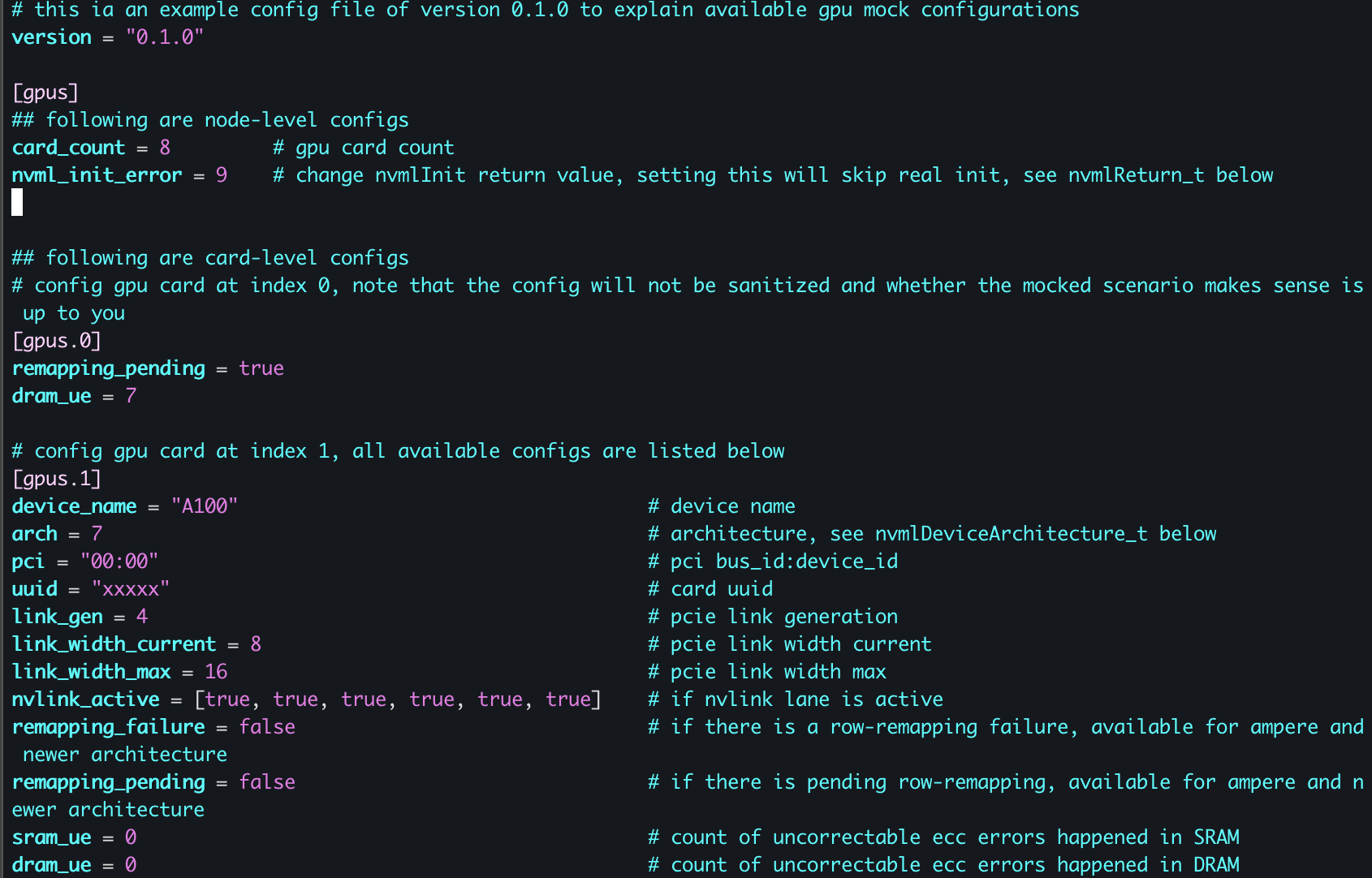
- GPU Failure Mock-Up Tools – Simulates GPU failures, enabling developers to test and build resilient AI frameworks that gracefully recover from hardware failures. Now, Nvidia GPUs and Ascend 910B NPUs are supported. We will extend support for more accelerators.
Here’s an example that it mocks the missing NvmlInit Error and diagnoses the GPU failure.
Building the Future of Scalable AI with AIBrix
Moving forward, we plan to continue exploring the co-design approach by developing initiatives such as standardizing the KV Cache API for use with external KV pools in prefix cache scenarios, plugging AIBrix distributed KV cache pool for Prefill & Decode (P&D) disaggregation, considering roofline-based models to streamline profiling processes in heterogeneous routing, and enhancing distributed orchestration to better support large-scale models like DeepSeek R1 and various offline scenarios.
AIBrix’s vision aligns with broader efforts to standardize LLM infrastructure, ensuring scalable and efficient AI deployments. As part of this mission, we actively collaborate with industry leaders to drive open, cloud-native solutions for LLM serving.
“ByteDance has been a phenomenal partner in helping Google drive standardization of LLM serving in Kubernetes through Working Group Serving and contributing to the Gateway API Inference Extension. We are excited to continue collaborating on shared components that will enable AIBrix and large scale inference platforms”
Clayton Coleman, Google Distinguished Engineer and Inference Lead for GKE
“vLLM has seen explosive growth worldwide, becoming a cornerstone of LLM inference. AIBrix is a promising project that builds on this momentum, offering powerful capabilities to scale and optimize vLLM for production deployments while driving innovation in open-source LLM inference.”
Robert Nishihara, Co-Founder of Anyscale & Co-Creator of Ray
Acknowledge
Many of our innovative ideas have been inspired by academic research, including works such as Preble, Melange, QLM and MoonCake. Integrating cutting-edge research into a production-grade system has been an enriching journey, enabling us to transform theoretical concepts into real-world applications. These contributions have significantly influenced our work, and we sincerely appreciate the researchers behind them—thank you! We’d also like to thank the vLLM community for their support in making AIBrix the control plane for vLLM, further strengthening our mission to build scalable and efficient AI infrastructure.
Originally open-sourced by ByteDance, AIBrix has rapidly evolved into a fully open-source project with contributions from the University of Michigan, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, University of Washington, Google, DaoCloud, and other industry and academic partners. Together, we are shaping the future of AI infrastructure through an open, collaborative approach, bridging cutting-edge research and real-world deployment expertise.
To start building your AI infrastructure with AIBrix, check out the https://github.com/vllm-project/aibrix and join our community and contribute to the future of open, scalable AI infrastructure.